Videos
The following videos (plus a few more) can be downloaded here.
All videos are released under a Creative Commons license.
Please credit: “Douglas Blackiston and Sam Kriegman”.
Designing CDOs.
Computers piece together biological building blocks into different structures. Most random configurations of the building blocks do not generate useful behavior. Eventually, evolution finds a good design.
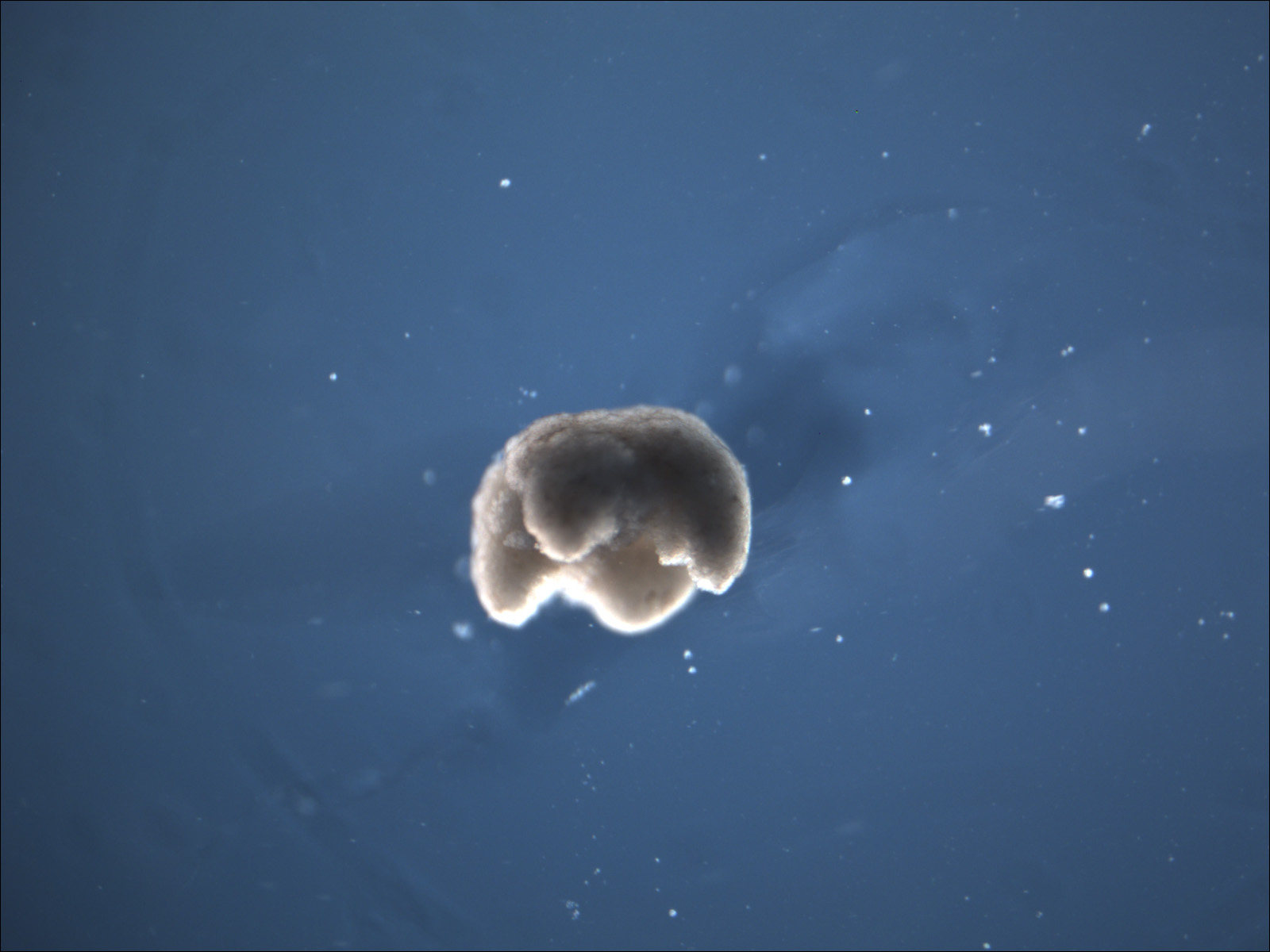
The good design found by the computer was built entirely out of frog cells. The behavior of the built organism matches the behavior predicted in simulation.
These organisms can automatically heal themselves after damage.
A swarm of CDOs collectively behave amid debris, in silico (inside the computer) and in vivo (as physical organisms).
An organism designed to manipulate (hold and push) an external object (particulate matter).
An organism that evolved to internally contain and transport an object of interest, simulating intelligent drug delivery.
Manufacturing CDOs.
The build process begins with the microinjection of fertilized Xenopus embryos (1.15-1.2mm in diameter) with synthetic mRNAs encoding lineage tracers (tdTomato (red) or GFPIII (green)) or proteins to alter cell fate (e.g. to produce heart muscle).
After developing for 24 hours at 14°C, the vitelline membrane is removed from each embryo with microsurgery forceps.
The animal cap of each embryo is then surgically excised with forceps and incubated for 10 minutes in dissociation media.
Next, the outer ectodermal layer (which does not dissociate) is manually separated from the inner cell layers (approximately 30μm in diameter).
The remaining tissue is gently agitated to further aid with dissociation, before being pooled with a micropipette.
Thousands of cells are transferred to agarose wells containing standard media (different cell types can be layer sequentially at this step), promoting cell re-aggregation.
Cell aggregates undergo compaction as they re-adhere...
..and are allowed to develop for two additional days at 14°C.
A microcautery device is utilized to define the rough shape of the transferred design (650μm-750μm in diameter).
Microsurgery forceps are then used to sculpt the final features: